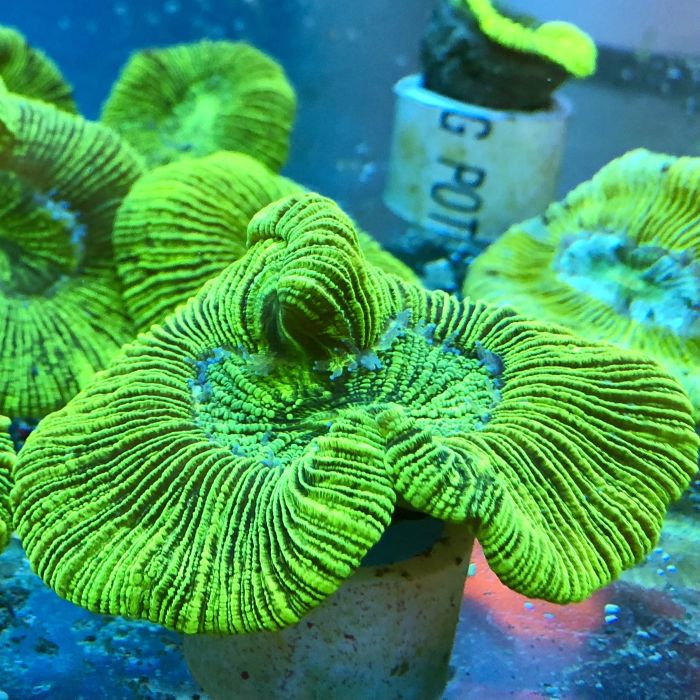
Brain Coral - Trachyphyllia
This coral receives most of its energy by utilizing the photosynthetic algae contained within its tissues. It will benefit from occasional feedings of meaty foods such as mysis shrimp, enriched brine shrimp, chopped krill, pellets, etc. Some corals may also respond to phytoplankton. Its transparent feeding tentacles extend mainly at night, although it can learn to feed during daylight hours.
Open brain corals are able to expand their tissues to a surprising size, and are often called Meat corals. They thrive under dim to moderate light, and may be damaged by intense illumination. They are often nipped on by fish, especially angelfish. Many open brains are sensitive to the chemicals released by soft corals, such as leathers, lemnalia and mushrooms; the use of carbon filtration (changed frequently) and regular water changes can minimize this.
Space should be provided between corals to allow for growth and expansion; although open brain corals possess feeding tentacles they are prone to being stung and damaged by neighboring corals.
This plump, single polyped coral is naturally free-living on the substrate; its pointed cone-shaped bottom helps to stabilize it in sand or rubble, and aids in differentiating it from the similar Wellso brain. It has some ability to rid itself of sand, however it takes a great deal of energy. Colored varieties are typically a beautiful green shade, and often fluorescence under actinic lighting; they may appreciate brighter light than red varieties. Trachy Brain is usually a round shape when small, and may develop folds as it matures.
Water flow is best provided as turbulent flow with the use of a wave maker or surge action. Constant laminar flow is very damaging and could cause death of the coral. Alkalinity, calcium, magnesium and strontium are required for growth and should be checked regularly.
- Difficulty: Intermediate
- Growth Speed: Slow
- Lighting: Low - Medium
- Average Placement: Low
- Water Flow: Low
- Temperament: Semi-Aggressive