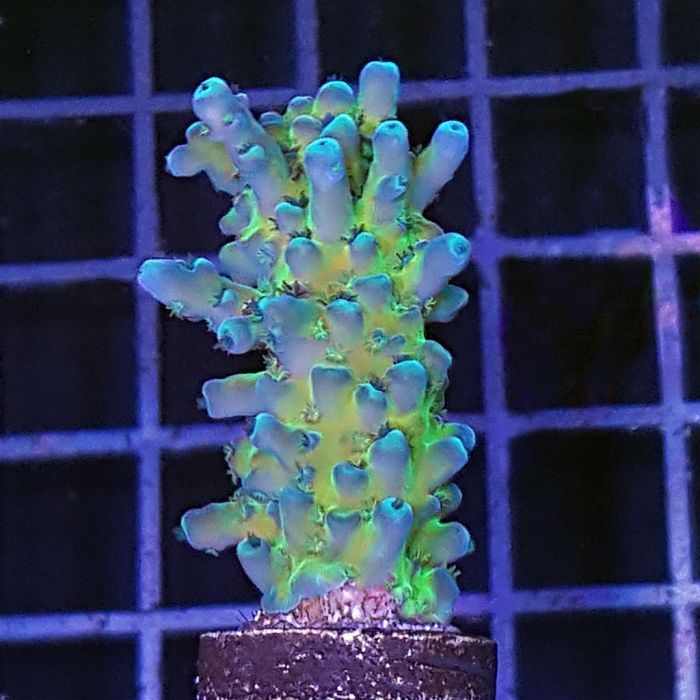
Acropora - Tort - Cali
Considered by many to be the pinnacle of reef-keeping success, Acropora corals are extremely demanding, but just as rewarding if given proper care. They require exceptionally stable water quality which can only be provided in a well-established aquarium over 6 months old. High levels of nitrate and phosphate are not tolerated and commonly cause browning; although low, stable levels are necessary for best growth and color. Alkalinity, calcium, magnesium and strontium are required for growth and should be checked regularly. Any instability leads to extreme stress which may lead to bleaching or tissue necrosis.
They are very prone to pests, such as the red bug copepod, gorilla crabs, vermetid and Drupella sp. snails, some Asterina sp. starfish, nudibranches, flat worms, and boring sponges. All colonies should be dipped prior to adding to a display aquarium. Quarantine and removal of any substrate are also beneficial practices. It may be host to several species of beneficial crustaceans including Tetralia and Trapezia sp. crabs.
Shallow water species have densely clustered polyps and need the brightest light, while those naturally from deeper water have sparse polyps with smooth skin and tolerate lower light levels. Newly acquired specimens should be acclimated to intense light levels slowly to avoid bleaching. Species with thicker branches demand the highest water flow. Acropora are related to Montipora but tend to be much more difficult to keep.
Space should be provided between corals to allow for growth and expansion nematocyst laden acontia filaments, which are digestive organs that can kill neighboring corals.
With a huge diversity of dazzling colors and shapes, it’s no wonder Acropora are some of the most popular corals of all. Colored Australian specimens are typically brighter and more impressively hued than those from other locations. It may be nearly any color of the rainbow, and many specimens are multicolored. Many species will display white or contrasting colored growth tips.
This coral receives most of its energy by utilizing the photosynthetic algae contained within its tissues. It will also benefit from occasional feedings of fine zooplankton and coral snow.
Temperature swings are not tolerated and may lead to bleaching. Temperatures should never be allowed to reach 82F, which will surely damage the colony. For this reason many aquarists keep their temperature lower as a precaution, as low as 76F.
Intermixing with soft corals (especially leathers, mushrooms and Lemnalia) is best avoided, as many soft corals release potent chemicals into the water which can be detrimental to the health of small polyp stony corals.
Water flow should be strong and is best provided as turbulent flow with the use of a wave maker or surge action. Alkalinity, calcium, magnesium and strontium are required for growth and should be checked regularly.
- Difficulty: Advanced
- Growth Speed: Medium
- Lighting: High
- Average Placement: Middle - High
- Water Flow: Medium - High
- Temperament: Semi-Aggressive